A new review uncovers how the prized truffle’s unique mix of antioxidants, polysaccharides, and sterols could make it more than a gourmet delicacy, positioning it as a potential ally in nutrition, medicine, and sustainable food innovation.

Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Potential of Truffles: A Comprehensive Review. Image Credit: kaicairone / Shutterstock
In a recent review published in the journal Antioxidants, researchers in Italy synthesized existing knowledge about the bioactive compounds in truffles and their biological properties. Their conclusions emphasize the potential of truffles as functional foods and natural sources of antioxidants.
The study also emphasizes the importance of advanced extraction and storage methods in preserving the bioactive integrity and quality.
Global Distribution and Functional Food Potential of Truffles
Truffles, the underground fruiting bodies of ectomycorrhizal fungi, are valued for their aroma, rarity, and nutritional richness. The review examined species from the genera Tuber, Terfezia, Tirmania, and Picoa, which support rural economies and forest ecosystems across North America, North Africa, Europe, and Asia.
Beyond their culinary importance, truffles possess significant biochemical diversity, making them promising candidates for functional food and therapeutic applications.
Recent discoveries, including an endogenous endocannabinoid system and novel polysaccharides, expand their pharmacological relevance. Technological advances in extraction and preservation now enable their use in nutraceutical and pharmaceutical formulations, broadening their market scope beyond gastronomy.
Macronutrients, Micronutrients, and Phytochemical Profile
Truffles are rich in carbohydrates and proteins but low in fats and fibers, providing essential minerals such as iron, magnesium, calcium, phosphorus, and potassium. Their lipid fraction, although limited, is dominated by unsaturated fatty acids, such as oleic and linoleic acids, and sterols like ergosterol and brassicasterol, which support antioxidant and cholesterol-lowering effects.
Structural polysaccharides, including β-glucans and heteropolysaccharides, exhibit immunomodulatory and antioxidant properties that are influenced by their molecular characteristics.
Phenolic compounds, such as cinnamic, coumaric, and gallic acids, and flavonoids like kaempferol and catechin, confer strong antioxidant capacity.
Desert truffles (Terfezia, Tirmania, Picoa) are richer in vitamin C, folate, vitamin E, and β-carotene, while European black and white truffles contribute B-vitamins and vitamin D precursors derived from ergosterol.
Notably, Tuber melanosporum contains the endocannabinoid anandamide, which may act as an olfactory attractant for mammal-mediated spore dispersal.
Bioactive Molecules and Nutritional Significance
Truffles offer high-quality, digestible proteins that contain all essential amino acids, with glutamate and sulfur-containing amino acids contributing to their distinctive umami flavor.
Bioactive peptides exhibit antioxidant, antihypertensive, and immune-regulatory effects. The characteristic aroma arises from volatile sulfur compounds, such as bis(methylthio)methane in white truffles and 1-octen-3-ol in black truffles, combined with aldehydes, ketones, and phenolic derivatives responsible for distinctive earthy or garlicky notes.
Truffle extracts exhibit a diverse range of biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, hepatoprotective, and anticancer effects. Terfezia claveryi extracts show hepatoprotective activity against CCl₄-induced toxicity, while certain Tuber and Terfezia species demonstrate anticancer properties via caspase-3 activation and HER2 oncogene suppression.
Additionally, truffle-derived compounds reduce oxidative stress, inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria, and protect hepatic and neural tissues through immune enhancement and the induction of apoptosis.
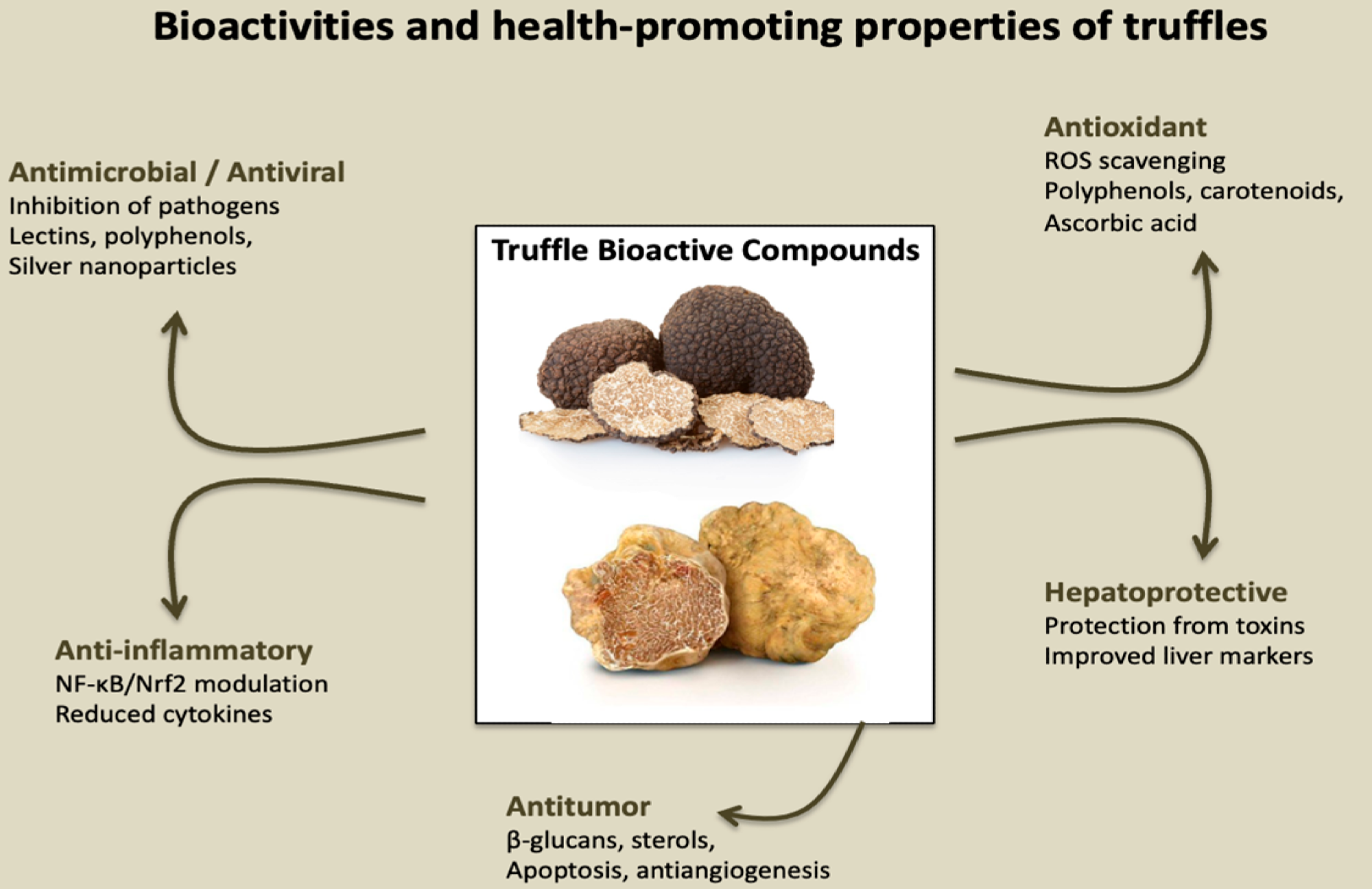
Bioactivities and health-promoting properties of truffles. Schematic representation of the main biological activities attributed to truffles and their bioactive compounds. Truffle-derived molecules, including polysaccharides, polyphenols, sterols, carotenoids, and terpenoids, exert multiple health-promoting effects. These properties include antimicrobial/antiviral activity, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, hepatoprotective functions, and antitumor potential. Such pleiotropic effects highlight the relevance of truffles not only as culinary delicacies but also as promising sources of nutraceutical and therapeutic agents.
Extraction Technologies for Bioactive Preservation
Preserving truffle bioactivity depends on efficient extraction and storage processes. Conventional solvent and Soxhlet extractions often expose heat-sensitive compounds, such as phenolics and volatiles, to degradation.
Modern green extraction methods, including ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE), pressurized liquid extraction (PLE), microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), and supercritical CO₂ extraction, enhance yield and purity while preserving antioxidant and sterol content. UAE and enzymatic pretreatment optimize polysaccharide recovery, whereas PLE efficiently isolates β-glucans and ergosterol under mild conditions.
Analytical techniques, such as headspace solid-phase microextraction (HS-SPME), enable the non-destructive identification of volatile compounds while maintaining their chemical integrity.
Storage and Preservation Strategies to Retain Quality
Post-harvest storage significantly impacts truffle composition and shelf life. Low-temperature storage and freezing slow spoilage but may alter aromatic compounds. Lyophilization best preserves bioactivity when combined with antioxidants or cryoprotectants.
Modified atmosphere packaging and edible coatings, such as chitosan or gum Arabic, minimize oxidation and microbial growth. Encapsulation using β- or γ-cyclodextrin and nano/microcarriers stabilizes volatile and antioxidant compounds.
Gentle technologies, including irradiation and high-pressure processing, extend freshness without compromising chemical integrity, ensuring truffles remain viable for food, nutraceutical, and pharmaceutical applications.
Therapeutic and Industrial Applications
Due to their antimutagenic, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory properties, truffles are gaining traction in the formulation of dietary supplements, dairy-based functional foods, and beverages.
Their extracts are increasingly utilized in cosmetics and perfumery due to their antioxidant and aromatic profiles. While most data are preclinical, future clinical trials and standardized extraction protocols will be crucial for validating therapeutic claims and ensuring reproducibility across products.
Sustainability, Cultivation, and Future Prospects
As demand increases, sustainability is critical, particularly for wild species such as Tuber magnatum, which face overharvesting pressures. Promoting sustainable cultivation practices, integrating traditional ecological knowledge, and advancing bioengineering approaches are essential for long-term viability.
Future research should focus on optimizing extraction and encapsulation technologies to enhance bioavailability and stability.
Ultimately, truffles represent not only gourmet delicacies but also emerging functional foods with potential preventive and therapeutic applications across the food, nutraceutical, and pharmaceutical industries.